ubiquitination
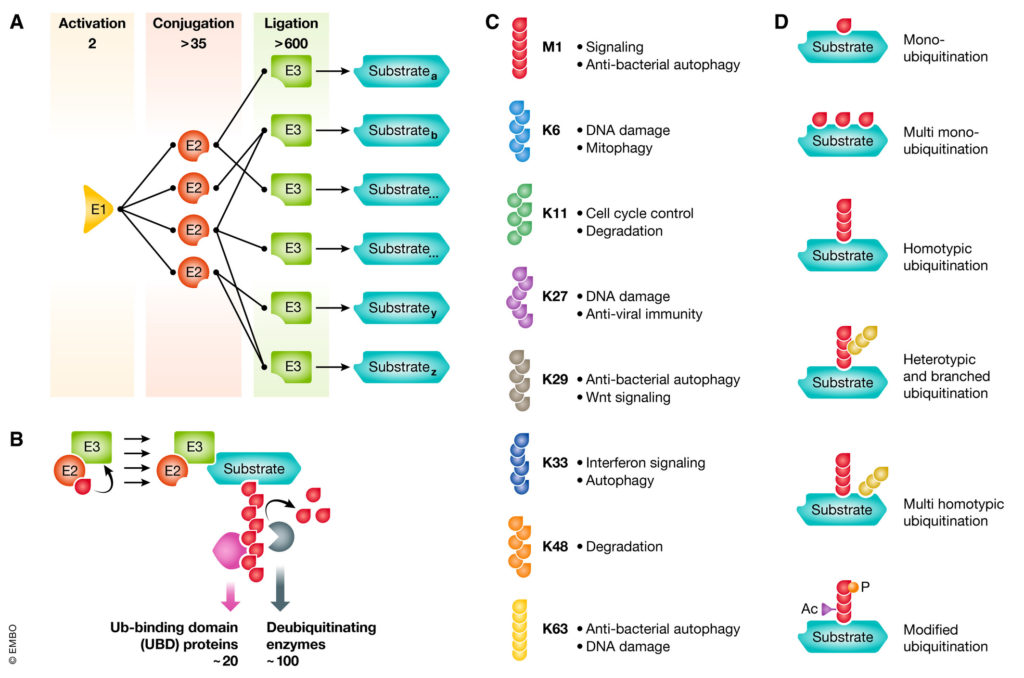
Ubiquitination is the post-translational modification of substrates with one or multiple ubiquitin (Ub) molecules and occurs through the coordinated action of a complex hierarchical system of enzymes, composed of Ub activating enzymes (E1s), Ub conjugating enzmyes (E2s) (van Wijk & Timmers, 2009) and Ub protein ligases (E3s) (van Wijk et al, 2009).
Ub conjugation is counteracted by deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) that hydrolyze chains as well as mono-Ub moieties. Ub signals are recognized by Ub-binding domain (UBD) proteins. Substrate modification can occur as single or multiple mono-Ub or as homotypic/heterotypic/branched chains, linked through Ub K6, K11, K27, K29, K33, K48 or K63, as well as M1 (linear or M1 Ub). The functional consequences of Ub signals is determined by cellular and substrate-context, Ub chain position, linkage type and conformation, leading to a plethora of responses, ranging from proteasomal degradation to non-proteolytic functions.
1. Development of novel tools to study cellular aspects of ubiquitination
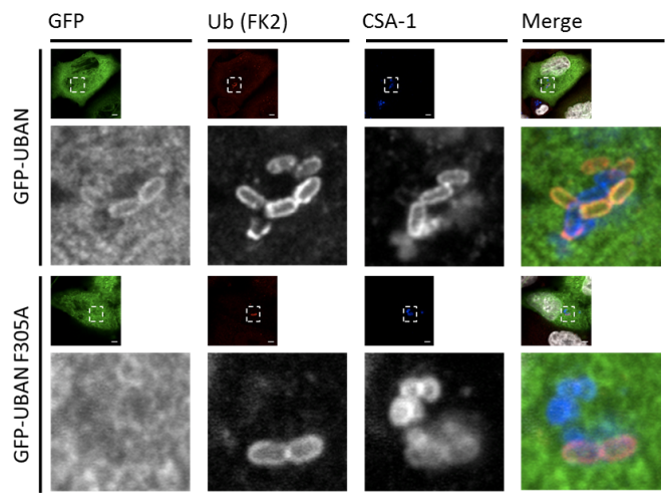
We have pioneered the development and application of genetic ubiquitin chain-specific fluorescent sensors based on naturally occuring UBDs, e.g. the M1 Ub-specific NEMO UBAN and the K63 Ub-specific TAB2 NZF. Ectopic expression of these sensors enabled the monitoring of Ub signals in fixed and living cells. Importantly, we observed K63-linked Ub during autophagic degradation of damaged mitochondria and M1-specific ubiquitination upon recognition and degradation of intracellular Salmonella (see Autophagy) (van Wijk et al 2012, van Wijk et al 2013, van Wijk et al 2017, van Wijk et al 2019). Furthermore, expression of these sensors deciphers the relevance of specific Ub signals upon TNFR1-mediated NF-kB activation and IL-1 activation.